Stroke Care
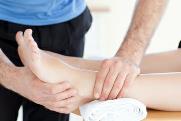
Progressive, dynamic and personal describe the essentials in the process of rehabilitation following a stroke. Therapy includes tone reduction and strengthening of the affected area. Exercises for hand, elbow and shoulder coordination are used for improving participation in daily activities. Therapy incorporates weight bearing on the affected side, improving balance and spatial awareness. Walking and transfer status is assessed and treated to improve the individual's progress toward independence. Some patients are seen immediately following their stroke while others may develop weaknesses or deficits years later. In either case, the patient is a candidate for skilled physical therapy assessment and appropriate intervention.
Neurological Care
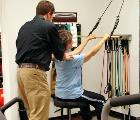
Neurological physical therapy is a discipline focused on working with individuals who have a neurological disorder or disease. In addition to the diagnosis of Stroke, other diagnoses include Alzheimer's disease, ALS, brain injury, cerebral palsy, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, spinal cord injury. Common problems of patients with neurological disorders include paralysis, vision impairment, poor balance, inability to ambulate, and loss of functional independence. Physical Therapy